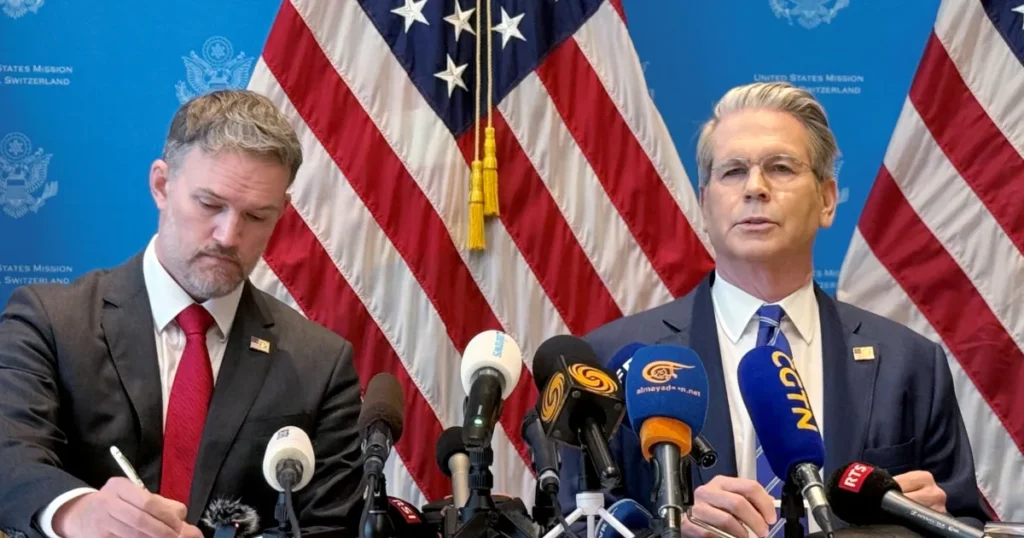
In a significant development for global trade, the United States and China have agreed to extend their existing 90-day tariff truce beyond its original expiration date of August 12, 2025. This decision, reached after two days of high-level negotiations in Stockholm, offers temporary relief to industries and markets that have been bracing for renewed economic friction. However, the extension remains conditional, hinging on final approval from U.S. President Donald Trump—a factor that injects uncertainty into an already fragile trade relationship.
Background: A Fragile Peace
The tariff truce was initially established to pause escalating duties between the two economic superpowers. Under the current arrangement, the U.S. has suspended its 30% tariffs on Chinese imports, while China has held off on its 10% tariffs on American goods. These measures were designed to create breathing room for both sides to negotiate more sustainable trade terms without further destabilizing global markets.
The Stockholm talks, hosted at the offices of Swedish Prime Minister Ulf Kristersson, brought together key figures including Chinese Vice Premier He Lifeng and U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent. Their goal: to find common ground on contentious issues that have long plagued bilateral relations.
Key Issues on the Table
While the extension of the truce is a welcome development, it does not signal a resolution to the deeper disputes between the two nations. Among the most pressing concerns discussed were:
- Iranian Oil Imports: The U.S. has expressed strong objections to China’s continued importation of oil from Iran, citing violations of international sanctions and geopolitical risks.
- Dual-Use Technology Exports: Washington remains wary of Chinese exports that could serve both civilian and military purposes, raising alarms about national security and intellectual property theft.
- Semiconductor Restrictions: The U.S. has imposed strict controls on semiconductor exports to China, aiming to protect its technological edge and prevent potential misuse.
These issues remain unresolved, and both sides acknowledged that further negotiations will be necessary to address them comprehensively.
Statements from Officials
U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent emphasized the tentative nature of the agreement, stating, “Nothing is agreed until we speak with [Trump].” His remarks underscore the pivotal role President Trump plays in finalizing the deal. Without his endorsement, the truce could collapse, and tariffs may revert to their previous levels or even escalate.
Chinese trade negotiator Li Chenggang confirmed that an extension had been agreed upon but declined to provide further details. This cautious approach reflects Beijing’s strategic posture—assertive yet measured—as it navigates the complexities of international diplomacy.
U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer highlighted the administration’s broader goals, including restoring domestic manufacturing and reducing trade deficits. “We’re committed to economic cooperation, but not at the expense of American jobs and innovation,” he said.
Strategic Leverage and Market Impact
Analysts note that China’s growing confidence in trade negotiations stems from its strategic leverage in key sectors. The country’s dominance in rare earth minerals and its expansive manufacturing capacity give it considerable influence over global supply chains. These assets could prove decisive in future rounds of talks, especially if the U.S. seeks concessions on technology and energy.
Despite the uncertainty surrounding Trump’s approval, markets have responded with cautious optimism. Industries exposed to tariff risks—such as automotive, electronics, and agriculture—have welcomed the temporary reprieve. Notably, cryptocurrency markets remained unaffected, as the discussions focused on macroeconomic stability rather than digital assets.
Global Implications
The extension of the tariff truce has broader implications for global trade and financial markets. While it offers short-term stability, the durability of the agreement remains in question. Previous negotiations, such as the May Geneva talks, provided temporary relief but failed to resolve underlying tensions.
If the truce holds, it could pave the way for more comprehensive trade agreements that address structural issues like intellectual property rights, market access, and regulatory transparency. However, if it falters, the fallout could be severe—triggering renewed tariffs, supply chain disruptions, and heightened geopolitical tensions.
What Comes Next?
All eyes are now on President Trump, whose decision will determine the fate of the extended truce. His administration has signaled a willingness to engage, but internal divisions and external pressures could complicate the approval process.
In the meantime, both nations are expected to continue backchannel communications and prepare for future negotiations. The stakes are high, and the path forward remains uncertain. But for now, the extension offers a glimmer of hope in an otherwise turbulent trade landscape.